What does business process automation mean?
Business process automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate repeatable, day-to-day tasks. BPA accelerates how work gets done by routing information to the right person at the right time through user-defined rules and actions. Thus, organizations can leverage this technology to streamline processes such as employee onboarding, accounts payable, contract management and more.
Why is business process automation important?
It isn’t just about replacing paper with PDFs—business process automation aims to make processes more cost-efficient, streamlined, error-proof and transparent. With automated processes in place, organizations save time and ensure best practices are implemented to improve overall operational efficiency.
What business processes should you automate?
Almost any business process you can think of can be enhanced in some way by automation. Still, some processes are better suited for automation than others. When assessing candidates for automation, you want may want to take a closer look at processes that are:
- Consistent across the organization.
- Repeatable.
- Require little room for error.
What are some examples of business process automation?
Below are three common business processes and how organizations drove positive change through automation:
HR Onboarding
Texas A&M University’s College of Engineering wanted to keep its commitment to increase student enrollment, but needed to hire new employees to manage this potential influx of students while keeping costs down. Their legacy HR onboarding process, however, was paper-driven and time-intensive. If the college was going to meet its goal, it needed to eliminate inefficiencies and streamline employee onboarding.
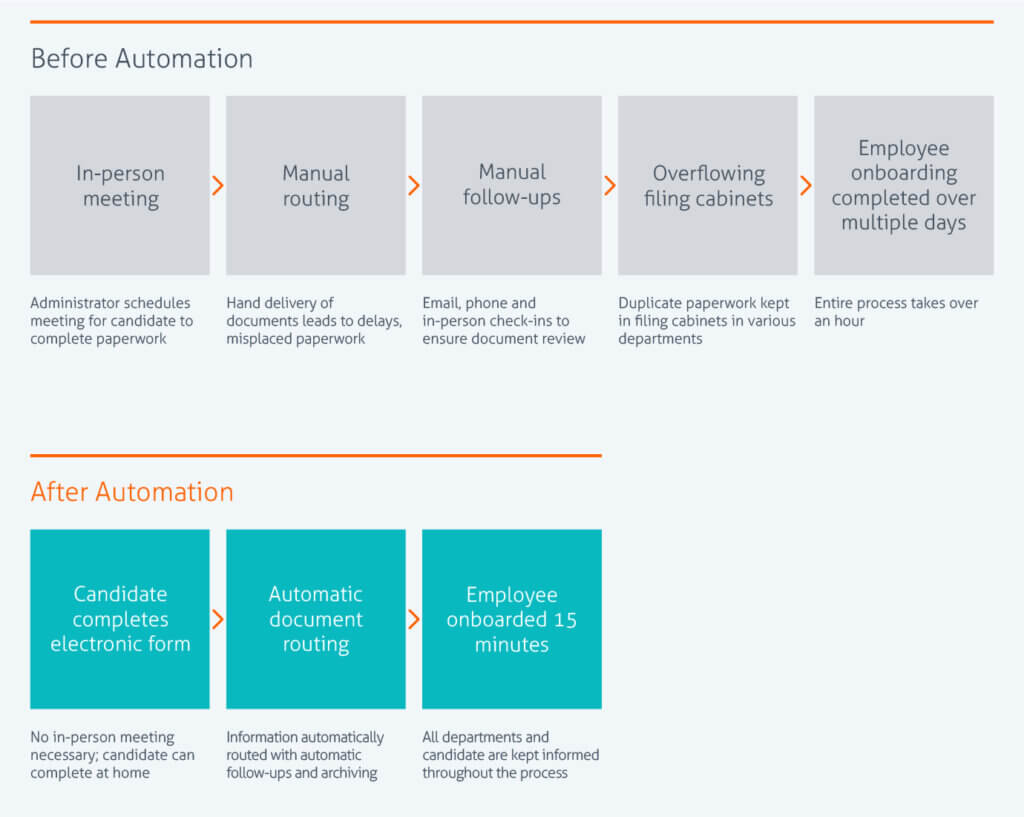
Automating HR onboarding with Laserfiche enabled the College of Engineering to hire more than 3,400 employees in a little over one year. Since its initiative’s success, other departments at Texas A&M have also began reengineering their own processes, sharing that successes campus-wide and creating a new culture of collaboration and innovation to make processes more efficient.
For more information on how your organization can find similar efficiencies, check out our guide to HR automation.
Accounts Payable
The City of Boca Raton’s accounts payable process relied heavily on paper invoices and copies being manually routed. Sometimes paper copies would be misplaced or delayed on someone’s desk, leading to unpaid invoices and upset vendors. Chasing down paperwork and answering phone calls from vendors was taking up employee time that could be better spent elsewhere.
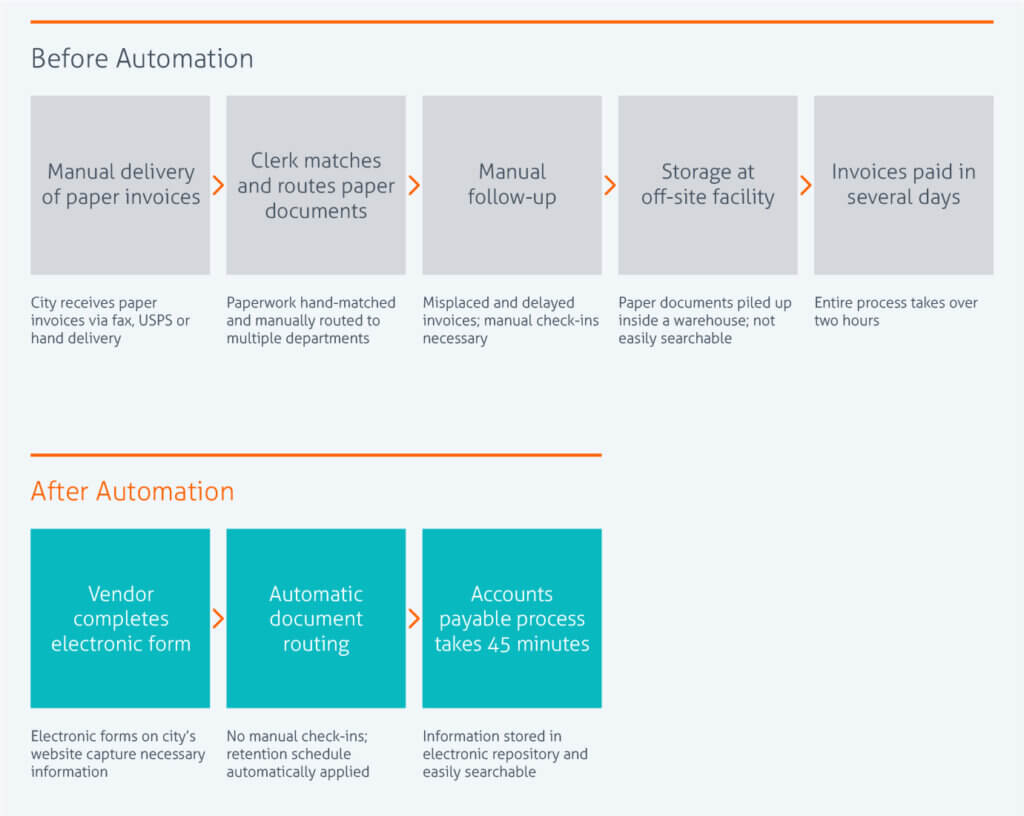
Leveraging business process automation, the city was able to track all its invoices from the moment they were received to final payment. The city significantly reduced processing errors while boosting customer satisfaction as a result of a faster and more efficient process.
For more information on how your organization can use business process automation to better manage invoice processing, check out our guide to accounts payable automation.
Contract Management
To continue its mission in keeping families out of poverty, non-profit organization Heifer International needed to increase efficiency and facilitate easier collaboration across its teams and partners worldwide. With documents built up from decades of work and hundreds of contracts requiring review per project, Heifer needed to centralize information and streamline contract management processes to help more people, faster.
By acquiring and deploying a system that could effectively automate processes, Heifer enabled its team members to collaborate on a worldwide scale on projects that help families, from Arkansas or Nepal. Legal contract reviews are streamlined, expediting the execution of projects including delivery of food and supplies. After its success implementing business process automation, Heifer continued to identify more back-office operations that could be made more efficient, freeing up resources for program initiatives.
How do I automate my business processes?
Most business process automation is done using a software platform. Choosing the right one can be a challenge, but once you do the rest is quite easy. Most have a low-code interface to help you design out how you want the process to work.
Then, once your process is created, you choose how it is triggered and what it outputs, such as a process that starts when you fill out a form and ends when you get a confirmation email. To that end, it is usually beneficial to have a process automation platform that is included in a robust document management solution, that includes a repository and forms functionality. Having process automation capabilities and the features that support them within the same software is far more convenient than having to bridge the connections with other solutions.
What is the difference between RPA and BPA?
Despite sounding similar, business process automation (BPA) and robotic process automation (RPA) are in practice quite different. RPA usually allows you to program a rudimentary software robot, or “bot” to perform basic data entry or other repetitive tasks to save time, usually using the same graphic user interfaces (GUIs) that users do. On the other hand, many BPA automations may be standalone or work on the backend of other software, outside a user interface, to retrieve information as needed.
While a bot may be easy to train by recording a human doing a repetitive task, a BPA solution may require more strategy and planning to implement effectively. Still, in many cases a BPA will likely cover a wider variety of uses cases and provide more end-to-end solutions. In fact, many BPA solutions may use RPA, but only as part of its broader functionality.
For an even deeper dive into the differences between RPA and BPA, check our our blog post here.
Customer Spotlight: Sky Telecommunications
Learn how the HR department at leading telecommunications company Sky was able to deliver more efficient services for its 25,000 employees by leveraging automation.
Browse customer reviews of Laserfiche on G2
Get insights from real customers on why Laserfiche is a top choice for organizations looking to streamline processes.
Continue your journey
Laserfiche has plenty of resources to help you find the right process automation platform and learn how to get the most out of the one you choose.
Discover Laserfiche’s 4 Steps to Innovation
Also be sure to check out the below infographic “Laserfiche 4 Steps to Innovation” to see how Laserfiche users can not only deploy solutions quickly, but get involved with a larger community of innovators.
Download the Process Automation Buyer’s Guide
You can also download our free resource, The Process Automation Buyer’s Guide for more background on what to look for in a process automation platform and how to procure the right solution:
Explore the Laserfiche Solution Marketplace
See how a robust process automation platform like Laserfiche can speed up the deployment of your solutions with process templates found on the Laserfiche Solution Marketplace. Visit the site to browse and download pre-built workflow templates for many everyday processes, including contract management, onboarding, front desk sign-ins and help desk requests.
Compare digital process automation vendors with G2
You can also check out the G2 Grid® for Digital Process Automation (DPA) to compare top vendors on the market. G2 is a website that collects and offers millions of business software reviews.





